Functional demands
Product properties and performance must conform to building standards, regulations and individual specifications, which take into consideration both present and future activities in the premises.

Product properties and performance must conform to building standards, regulations and individual specifications, which take into consideration both present and future activities in the premises.
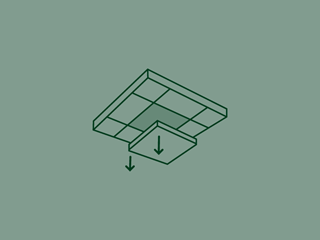
Ecophon offers ceiling systems with full demountability, even with concealed suspension systems.
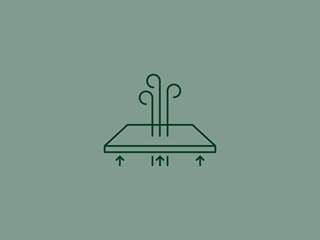
Some areas, for example clean rooms, require the indoor air pressure to be controlled.

Life Cycle Analyses of Ecophon products are conducted in line with ISO 14040 and give a transparent overview of our environmental impact.

Ecophon ceiling systems are CE marked according to the European harmonized standard EN13964:2014.

Some specific Ecophon products have been designed to withstand the use of common detergents and disinfecting agents.

Some Ecophon products have been classified according to ISO 14644-1:2015 to ensure their compatibility with clean room requirements.

Cleaning methods for Ecophon systems and what to consider to avoid unnecessary soiling.
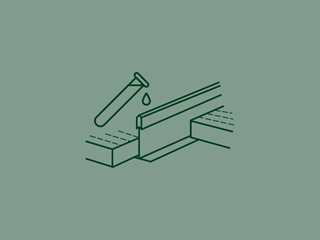
All Ecophon grid systems have been developed to meet the basic level of requirements regarding corrosion, specific products meet higher requirements.

Fire safety requirements for suspended ceilings, fire safety design and fire testing and classification of products.

Ceiling producers must ensure that ceiling tiles have sufficient strength to support their own weight once installed, and potentially an additional point/linear/distributed load.

Impact resistance of Ecophon products is tested according to EN 13964:2014 (ceiling products) and DIN 18032-3 (wall panels).

The VOC content of Ecophon products is tested by external laboratories in accordance with European regulations.

Lighting properties for Ecophon adapted lighting products.

Mechanical properties including loading capacities and general guidelines for Ecophon grids and ceilings.

Ecophon products have been tested to ensure they do not serve as a natural breeding medium for mould and bacteria.

To ensure the durability of the surface after repeated cleaning, some specific Ecophon products have been evaluated according to ISO 11998:2006.

The interaction of acoustics and modern cooling technologies, such as TABS and lightweight cooling systems.

Visual appearance and light highly impacts the overall look and feel of a room.